So you’ve decided that you want to get tested to see if you have Celiac disease. Good for you! But what does a Celiac disease test entail? It actually depends on the kind of test you decide to take, and how certain of the diagnosis you want to be. Remember: these tests are for Celiac disease only - they won’t give you an answer on other conditions like gluten intolerance or sensitivity. Here are the three most commonly used tests for Celiac!
Antibody Tests
Flickr user Iqbal Osman1
People with Celiac disease have a significantly higher level of Celiac antibodies in their blood, so the simplest way to test for Celiac is just to check the level of antibodies with what’s called a tTG-IgA blood test. This test is pretty sensitive - around 98% accurate. The catch? You have to be eating a diet containing gluten for the test to work, since the Celiac antibodies have to be present in order to be detected.
However, false positives aren’t out of the question for an antibody test, and if you have other autoimmune disorders you’re also more likely to get a false positive. You’ll also need a small intestine biopsy to know that the antibody test is correct, but it’s a way to get an idea without jumping right into an invasive test.
There’s also a chance for a false negative if you haven’t been on a gluten diet long enough to build up the antibodies. So if you want to be even more certain, there are a few other ways to check.
Endoscopy
Flickr user euthman
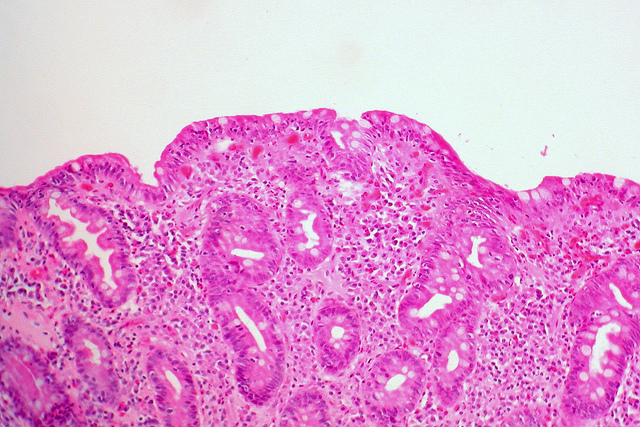
While significantly less fun, an endoscopy can far more accurately confirm Celiac disease if there’s a cause for doubting a blood test. An endoscopy allows doctors to take an actual look at the lining of your small intestine to see if there’s inflammation.
Sometimes doctors will recommend an endoscopy even if you do test positive with a blood test, just to be sure. The endoscopy can also tell you if you have another condition similar to Celiac, like gluten sensitivity. And like with a blood test, you have to be eating gluten at the time of the procedure.
Genetic Testing
Flickr user CIAT International Center for Tropical Agriculture
Though it might sound a little intense on the surface, a genetic test for Celiac is actually pretty simple for you - it can be done with a blood sample or saliva. The difference with a genetic test is that it can help indicate Celiac disease if you’re already on a gluten-free diet. Like with an antibody test, you’ll need a small intestine biopsy to completely confirm Celiac after a genetic test. The genetic test is also a useful way for close relatives of people diagnosed with Celiac disease to see if they’re a carrier for the disease or will develop it later.
What Celiac disease test did you take? What was the experience like for you? Tell us in the comments below!